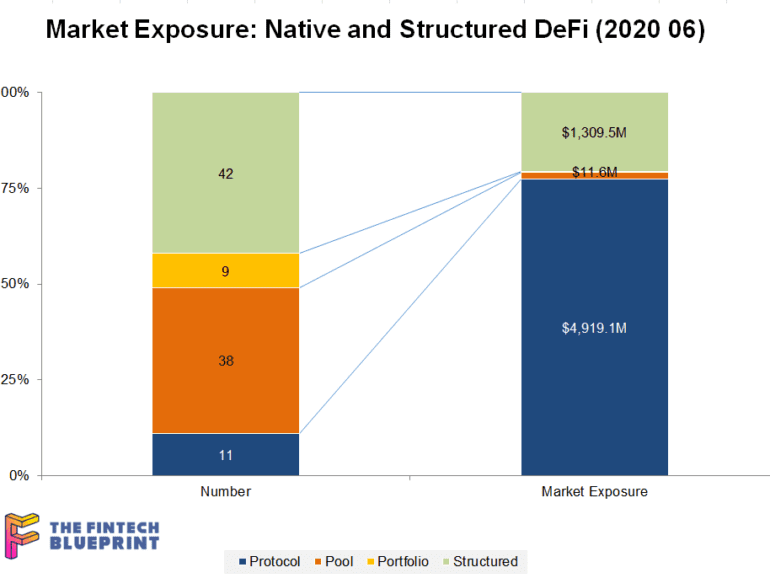
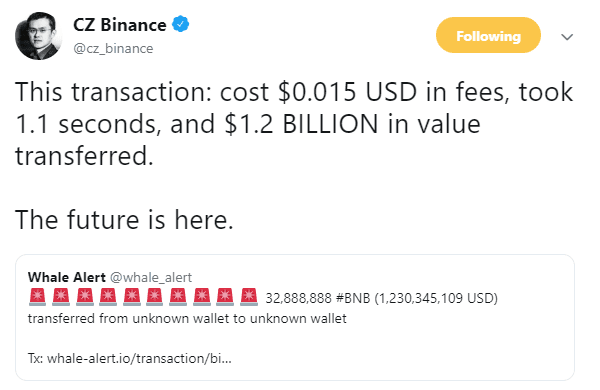This week, I grapple with the concepts of financial centralization and decentralization, anchoring around custody, staking, and DeFi examples. On the centralized side, we look at BitGo's acquisition of Lumina, Coinbase Custody and its similarity to Schwab and Betterment Institutional. On the decentralized side, we examine the recent $500 million increase in value within the Compound protocol, as well as the recursive loops that could pose a broader financial risk to the ecosystem.
I presented earlier this week at the Ally Invest virtual conference, and the prompt asked for a description of what happens to finance from Fintech to Crypto / Blockchain to Augmented Reality / Virtual Worlds and finally to Artificial Intelligence.
In this conversation, we chat with Gabriel Anderson – Managing Director at Tachyon, Head of Market Strategy & Business Intelligence at ConsenSys Labs. Former Head of VaynerMedia. Alumnus of Merrill Lynch.
More specifically, we touch on what Tachyon is, how it works, and who it’s for, the growth of crypto, and what needs to come next to allow the widespread adoption of crypto by mainstream society. Gabriel talks about the best projects he has seen so far that combine NFTs with other elements of DeFi and crypto, and what he’d like to see more of in the future.
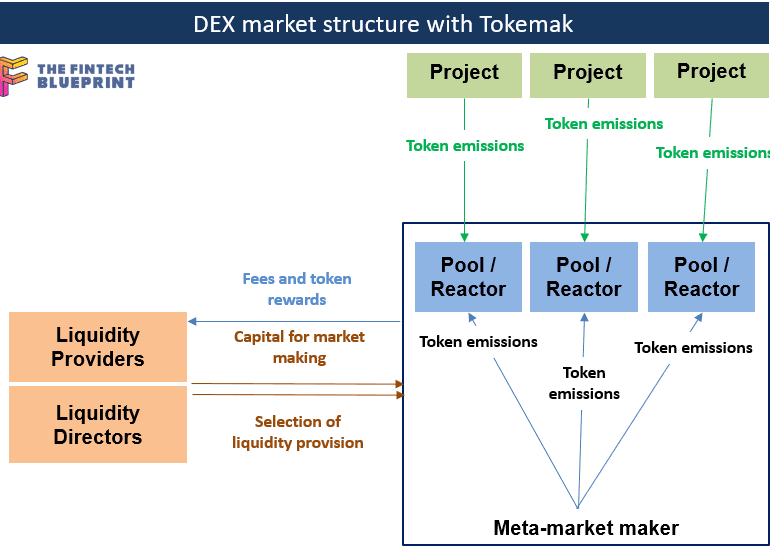
This week we continue the discussion of the shape of DeFi 2.0. We highlight Tokemak, a protocol that aims to aggregate and consolidate liquity across existing projects. Instead of having many different market makers and pools across the ecosystem, Tokemak could provide a clear meta-machine that optimizes rewards and rates across protocol emissions. This has interesting implications for overall industry structure, which we explore and compare to equities and asset management examples.
The web of investment bank technology, there are 20 or more core vendors on which systems run. Adding Blockchain to the mix merely adds a 21st system, which is by design incompatible with everything else. Thus enterprise chain projects have been focusing on integration and proofs of concepts, not re-engineering the core. But we know how this plays out -- as it has over and over again across Fintech. Digitizing "unimportant" channels and hoping for them to succeed simply doesn't work. See JP Morgan giving up on Finn, or Northern Trust capitulating its pioneering idea into Broadridge, or any other number of examples from Bloomberg to LPL Financial. Even the struggles of Digital Asset could be used as an example of the danger of working oneself into an existing web of solutions, and trying to preserve their dependencies.
This week, we cover these ideas:
Crypto prices show increasing correlation in market swings, which hides the large substantive differences between projects
The core narrative of Bitcoin, and its fundamental indicators
The core narrative of Ethereum and Web3, and its fundamental indicators
A sanity check on potential market caps relative to gold, equities, and other assets
While the future of payments is digital, Gnosis Pay co-founder and CEO Marcos Nunes said that leaves plenty of room for consumer choice.
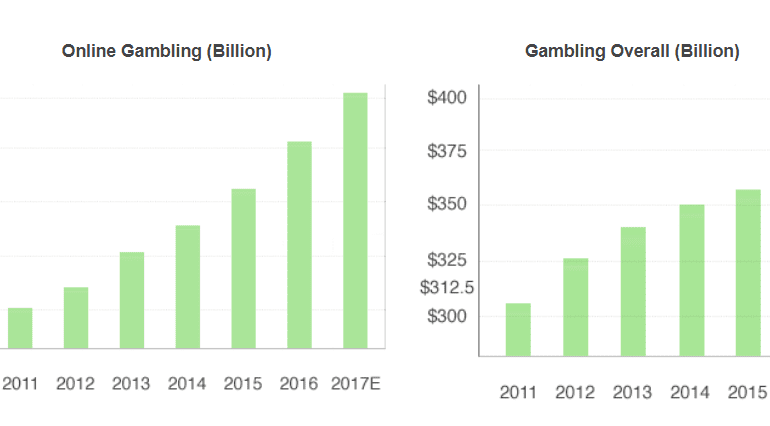
Looking into the statistics of gambling is illuminating and depressing. The UK, where gambling is more widely accepted than in the US, sees rates of 40-60% across all adults according to 2016 research. Revenues for casinos are over $100 billion annually, and global gambling revenues, including sports betting and the national lotteries, amount to over $400 billion. That's like the equivalent of the entire software cloud industry. And it asymmetrically addicts and disadvantages the already disadvantaged (see academic research here, here, and here).
In this conversation, we talk with Camila Russo of The Defiant and author of The Infinite Machine, about her journey as a successful financial journalist was derailed by the Crypto boom and subsequent winter of 2017. Additionally, we explore the success behind her first book, the nuances of the NFT craze, and how The Defiant became one of the most popular crypto media brands to date.
In this conversation, we talk with Mike Belshe, CEO of BitGo and expert technologist about custody, prime brokerage, and the evolution of the institutional digital asset industry.
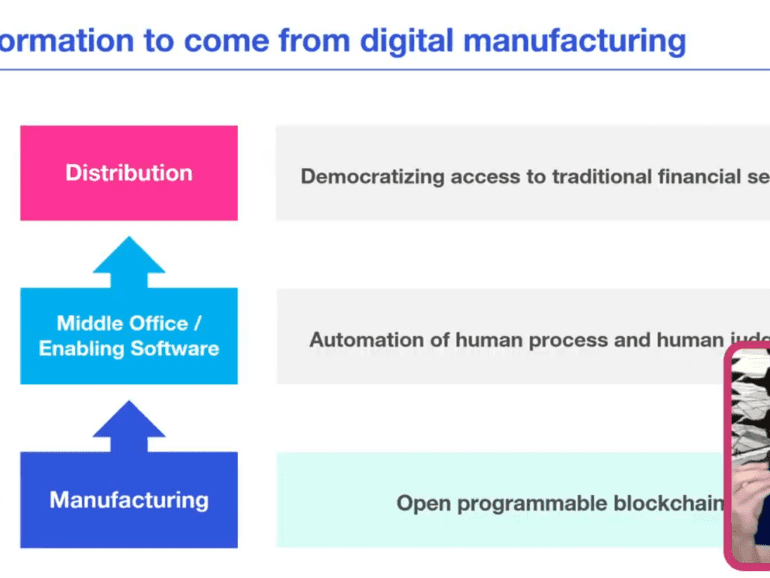
I often mention that crypto is still all about capital markets trading (i.e., manufacturing) and not about wealth management (i.e., distribution). This conversation touches on where we are in the maturity of market infrastructure, the role of fiduciaries, and the path forward. If you are sitting in a RIA, investment fund, or other asset manager, pay attention!