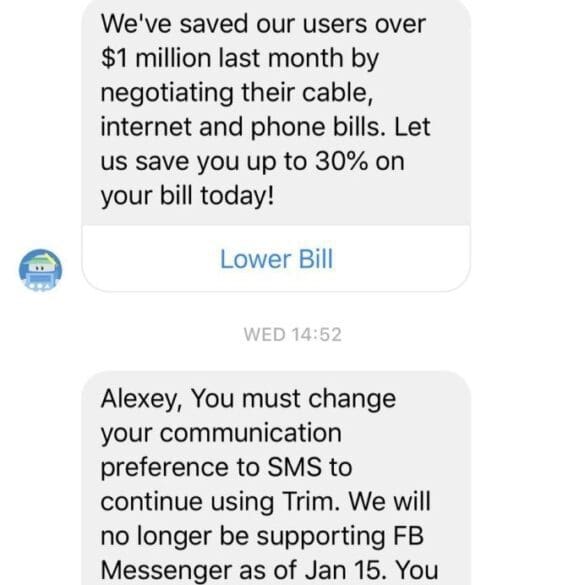
In the long take this week, I try out a contrarian point of view on personal finance chatbots. Trim, a savings chatbot, just withdrew support from Facebook Messenger. While lots of other chatbots are still invested in conversational banking, what could we take away from the counterfactual of chatbots failing to get B2C traction? What is the impact on the rest of the platform wars waged by Amazon, Google, and Tesla for connected homes, cars, and the Internet of Things?
2019 saw a number of big moves from big tech companies when it came to financial services and 2020 is...
I started writing about marketplace lending back in 2010, so I have spent almost the entire decade immersed in this...
Finance is everywhere, and everywhere is finance. Smart city supply chains, self driving car insurance, video game real estate markets -- no matter which frontier technology you touch, it will have embedded implications on the delivery of financial services. And why wouldn't it? Like the use of language, finance is a human technology that allows societies to coalesce and compete with one another (in the Yuval Harari sense). It lifts people out of poverty and into entrepreneurship through microloans, providing generational sustenance for their families. And of course it also throws them into pits of corruption and greed, as they drink too deeply from the rivers of securitization and political power.
But enough poetry! I want to talk about augmented reality, attention platforms, and the re-formulation of payments and lending propositions in a global context.
Amazon has partnered with Synchrony Financial in order to launch the Amazon Credit Builder which targets customers who have no...
Anyone watching Fintech over the last decade has recognized an increasing shift of power from product manufacturers to the platforms where those products are sold. In the case of Amazon, Google, and Facebook -- finance is just a feature among thousands of others. I've made this point since 2017, when Amazon launched lending into its platform. Brett King has been a bit more generous in the categorization, calling the shift "embedded banking". This means that banking products are built into you life's journey, not accessed in a separate customer center location. The financial API trend is a tangible symptom of this vector.
BBVA has announced a partnership with Amazon; the partnership is first focused on selling physical products but it’s clear that...
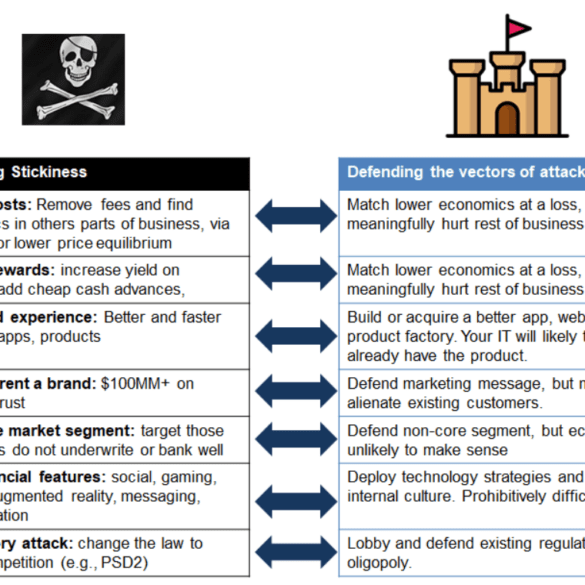
Today's corporations and governments are in the business of defining the balance of these aspects of our participation in society and the economy. Beliefs about the immutability of different attributes about what makes a person (or an employee) and how economies are built (cutting the pie, vs. growing the pie) determine the policy decisions you make, top down. As the core example this week, let's take Deutsche Bank. Facing pricing pressure and headwinds in several of its businesses, Deutsche is responding with a plan to fire 18,000 employees by 2022 and an announced investment of €13 Billion in technology and innovation by 2022. They even spun up a hipster-colored neobank as a proof point. Wall Street ain't buying it.
JP Morgan just shut down its neobank competitor Finn, targeted at Millennials in a smartphone app wrapper. Several other traditional banking incumbents have similar efforts, from Wells Fargo's Greenhouse, Citizens Bank's Citizens Access, MUFG's PurePoint and Midwest BankCentre's Rising Bank, as well as most of the Europeans (e.g., RBS competition to Starling called Mettle). These banks have every advantage -- from product infrastructure, to balance sheet, to regulatory licenses, to physical footprint, to relationships with the older generation. So how is it that players like Chime, MoneyLion, Revolut, and N26 are all able to get millions of happy users and the incumbents are failing?
Tearsheet asked 107 financial professionals from traditional financial institutions and fintechs who is the biggest threat to banks in consumer...